RZ-G/RZ-G2 Communications: Difference between revisions
(Bluetooth Support) |
|||
| Line 951: | Line 951: | ||
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " wpa-supplicant " | IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " wpa-supplicant " | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
= Bluetooth Support = | |||
Revision as of 20:30, 30 May 2023
← RZ-G
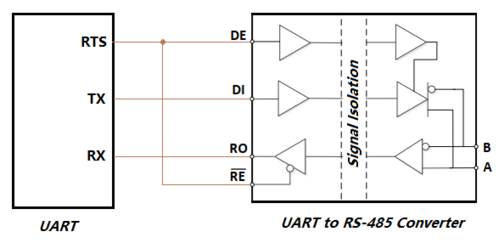
- This page is to discuss things about commonly used communication interfaces of RZ/G2 MPU. Currently, RS-485 half-duplex is added only.
RS-485 half-duplex communication
- RS-485 half-duplex communication is widely used. But lots of MPUs can not support RS-485 directly, they support UART full-duplex communication commonly. Renesas RZ/G2 series MPU integrates SCIF(i.e UART) which also can not support RS-485 directly. But we can implement RS-485 half-duplex communication by SCIF with a UART-to-RS485 converter IC. Typical block diagram is as follows.
Because the RS-485 converter is working at transmitter mode(controlled by DE pin) or receiver mode(controlled by /RE pin). RZ/G2 series MPU's SCIF can not support this kind of mode switching by hardware, so we need to use a GPIO to realize it.
Here, the RTS signal of UART of RZ/G2 MPU is a part of SCIF peripheral signals, but it is used for modem feature. So we just configure it as a GPIO. The DE and /RE signals of the converter are always opposite. Users can select one other GPIO to replace RTS(GPIO) or select two other GPIOs to control DE and /RE separately.
Following description will show the RS-485 feature support on Renesas RZ/G2L MPU. Simply speaking, we just need to add GPIO control code in the kernel driver code. That is driving the GPIO to HIGH at the beginning of data transmission and driving the GPIO to LOW at the end of data transmission. In data receiving mode, the code is not needed to be changed. The device tree, tty driver and SCIF driver inside kernel will be modified. The tty driver is shared by a lot of applications(ssh, telnet, serial, etc), so we must carefully check and add necessary judgment. The user space application code does not need to care about the GPIO control. It just needs to read and write the UART device simply as if the RS-485 half-duplex is supported by hardware.
The commonly concerned thing is the point of driving GPIO to LOW. Or the interval between the last STOP bit of MPU sending data and the RS-485 device’s first START bit. The device side may send back some data to MPU quickly after it received some data, and this interval may be less than 10us. If the GPIO was not driven to LOW in time some data from the device will be lost. In fact, this interval is RS-485 device or protocol specific. This time between the last STOP bit of sending data and driving GPIO to LOW on RZ/G2L SMARC board is around 10 ~ 20us. But it is only for reference, this interval may be affected by lots of things(CPU load, real-time tasks, interrupts latency, etc).
Another thing needs to be mentioned is that the read out data size by application’s single read(). The default RZ/G2 SCIF driver implementation supports reading out 8 bytes at most for a single read() in application. It is not an issue or bug. But some users want to read out data as many as possible by a single read(). The following code can support this kind of usage. Please refer to the patch of sci_transmit_chars() function. In fact, there is still a limitation. And the limitation depends on the kernel tty driver’s circular buffer size whcih is often very big(over 1024).
Preconditions:
- Linux kernel is 5.10 cip13-rt5, VLP3.0.1.
- SCIF2 is used.
- SCIF DMA must be disabled(using PIO mode).
- RTS pin of SCIF2 is used as the GPIO.
arch/arm64/boot/dts/renesas/rzg2l-smarc-pinfunction.dtsi
diff --git a/arch/arm64/boot/dts/renesas/rzg2l-smarc-pinfunction.dtsi b/arch/arm64/boot/dts/renesas/rzg2l-smarc-pinfunction.dtsi
index a3ca3709db80..6cd6ae776dd6 100644
--- a/arch/arm64/boot/dts/renesas/rzg2l-smarc-pinfunction.dtsi
+++ b/arch/arm64/boot/dts/renesas/rzg2l-smarc-pinfunction.dtsi
@@ -62,8 +62,8 @@ scif0_pins: scif0 {
scif2_pins: scif2 {
pinmux = <RZG2L_PORT_PINMUX(48, 0, 1)>, /* TxD */
<RZG2L_PORT_PINMUX(48, 1, 1)>, /* RxD */
- <RZG2L_PORT_PINMUX(48, 3, 1)>, /* CTS# */
- <RZG2L_PORT_PINMUX(48, 4, 1)>; /* RTS# */
+ <RZG2L_PORT_PINMUX(48, 3, 1)>; /* CTS# */
+ /*<RZG2L_PORT_PINMUX(48, 4, 1)>;*/ /* RTS# */
};
#endif
arch/arm64/boot/dts/renesas/rzg2l-smarc.dtsi
diff --git a/arch/arm64/boot/dts/renesas/rzg2l-smarc.dtsi b/arch/arm64/boot/dts/renesas/rzg2l-smarc.dtsi
index 4f1828caf097..056b0db3cc42 100644
--- a/arch/arm64/boot/dts/renesas/rzg2l-smarc.dtsi
+++ b/arch/arm64/boot/dts/renesas/rzg2l-smarc.dtsi
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
#include <dt-bindings/pinctrl/rzg2l-pinctrl.h>
/* comment the #define statement to disable SCIF2 (SER0) on PMOD1 (CN7) */
-//#define PMOD1_SER0 1
+#define PMOD1_SER0 1
/ {
aliases {
@@ -36,7 +36,9 @@ &scif2 {
pinctrl-0 = <&scif2_pins>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
- uart-has-rtscts;
+ rs485-sw-rts;
+ gpios = <&pinctrl RZG2L_GPIO(48, 4) GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
+ /*uart-has-rtscts;*/
status = "okay";
};
#endif
drivers/tty/serial/serial_core.c
diff --git a/drivers/tty/serial/serial_core.c b/drivers/tty/serial/serial_core.c
index 32d09d024f6c..7ee95d22ce3f 100644
--- a/drivers/tty/serial/serial_core.c
+++ b/drivers/tty/serial/serial_core.c
@@ -1434,6 +1434,17 @@ uart_ioctl(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
if (ret != -ENOIOCTLCMD)
goto out;
+ switch(cmd)
+ {
+ case TIOCSSWRTS:
+ uport = state->uart_port;
+ ret = uport->ops->swrts_ctl(uport, arg);
+ goto out;
+
+ default:
+ break;
+ }
+
mutex_lock(&port->mutex);
uport = uart_port_check(state);
@@ -2556,6 +2567,12 @@ static const struct tty_port_operations uart_port_ops = {
.shutdown = uart_tty_port_shutdown,
};
+int is_serial_core_tty(struct tty_struct *tty)
+{
+ return ((tty->ops == &uart_ops) && tty->ops->ioctl(tty, TIOCSSWRTS, SWRTS_GET_I));
+}
+EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(is_serial_core_tty);
+
/**
* uart_register_driver - register a driver with the uart core layer
* @drv: low level driver structure
drivers/tty/serial/sh-sci.c
diff --git a/drivers/tty/serial/sh-sci.c b/drivers/tty/serial/sh-sci.c
index 626b5507d1ed..b416574bad3e 100644
--- a/drivers/tty/serial/sh-sci.c
+++ b/drivers/tty/serial/sh-sci.c
@@ -48,6 +48,9 @@
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/tty_flip.h>
+#include <linux/gpio.h>
+#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
+#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#ifdef CONFIG_SUPERH
#include <asm/sh_bios.h>
@@ -157,6 +160,11 @@ struct sci_port {
bool has_rtscts;
bool autorts;
+
+ int rs485_sw_rts;
+ int sw_rts_gpio;
+ int sw_rts_count;
+ struct semaphore sw_rts_sema;
};
#define SCI_NPORTS CONFIG_SERIAL_SH_SCI_NR_UARTS
@@ -609,7 +617,7 @@ static void sci_stop_tx(struct uart_port *port)
if (port->type == PORT_SCIFA || port->type == PORT_SCIFB)
ctrl &= ~SCSCR_TDRQE;
- ctrl &= ~SCSCR_TIE;
+ ctrl &= ~(SCSCR_TIE | SCSCR_TOIE);
serial_port_out(port, SCSCR, ctrl);
@@ -805,6 +813,7 @@ static int sci_rxfill(struct uart_port *port)
static void sci_transmit_chars(struct uart_port *port)
{
struct circ_buf *xmit = &port->state->xmit;
+ struct sci_port *sport = to_sci_port(port);
unsigned int stopped = uart_tx_stopped(port);
unsigned short status;
unsigned short ctrl;
@@ -839,6 +848,9 @@ static void sci_transmit_chars(struct uart_port *port)
serial_port_out(port, SCxTDR, c);
port->icount.tx++;
+
+ if(sport->rs485_sw_rts)
+ sport->sw_rts_count--;
} while (--count > 0);
sci_clear_SCxSR(port, SCxSR_TDxE_CLEAR(port));
@@ -846,7 +858,7 @@ static void sci_transmit_chars(struct uart_port *port)
if (uart_circ_chars_pending(xmit) < WAKEUP_CHARS)
uart_write_wakeup(port);
if (uart_circ_empty(xmit))
- sci_stop_tx(port);
+ serial_port_out(port, SCSCR, (serial_port_in(port, SCSCR) & ~SCSCR_TIE) | SCSCR_TOIE);
}
@@ -856,71 +868,98 @@ static void sci_transmit_chars(struct uart_port *port)
static void sci_receive_chars(struct uart_port *port)
{
struct tty_port *tport = &port->state->port;
- int i, count, copied = 0;
+ struct sci_port *sport = to_sci_port(port);
+ int i, count, copied = 0, rx_to;
unsigned short status;
unsigned char flag;
+ if(1 == sport->rx_trigger)
+ dev_warn(port->dev, "rx trigger '1' is too low, no DRI interrupt\n");
+
status = serial_port_in(port, SCxSR);
- if (!(status & SCxSR_RDxF(port)))
+ if (!(status & (SCxSR_TEND(port) | SCxSR_RDxF(port))))
return;
- while (1) {
- /* Don't copy more bytes than there is room for in the buffer */
- count = tty_buffer_request_room(tport, sci_rxfill(port));
+ /*
+ TEI & DRI share interrupt vector
+ Priority: TEI > DRI
+ Return after TEI handling, let CPU handles next interrupt(maybe DRI).
+ */
+ if(status & SCxSR_TEND(port)) {
+ if(sport->rs485_sw_rts && (sport->sw_rts_count <= 0)) {
+ gpio_set_value(sport->sw_rts_gpio, 0);
+ up(&sport->sw_rts_sema);
+ }
- /* If for any reason we can't copy more data, we're done! */
- if (count == 0)
- break;
+ sci_clear_SCxSR(port, SCxSR_TEND_CLEAR(port));
+ sci_stop_tx(port);
- if (port->type == PORT_SCI) {
- char c = serial_port_in(port, SCxRDR);
- if (uart_handle_sysrq_char(port, c))
- count = 0;
- else
- tty_insert_flip_char(tport, c, TTY_NORMAL);
- } else {
- for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
- char c;
-
- if (port->type == PORT_SCIF ||
- port->type == PORT_HSCIF) {
- status = serial_port_in(port, SCxSR);
- c = serial_port_in(port, SCxRDR);
- } else {
- c = serial_port_in(port, SCxRDR);
- status = serial_port_in(port, SCxSR);
- }
- if (uart_handle_sysrq_char(port, c)) {
- count--; i--;
- continue;
- }
-
- /* Store data and status */
- if (status & SCxSR_FER(port)) {
- flag = TTY_FRAME;
- port->icount.frame++;
- dev_notice(port->dev, "frame error\n");
- } else if (status & SCxSR_PER(port)) {
- flag = TTY_PARITY;
- port->icount.parity++;
- dev_notice(port->dev, "parity error\n");
- } else
- flag = TTY_NORMAL;
-
- tty_insert_flip_char(tport, c, flag);
+ return;
+ }
+
+ rx_to = SCIF_DR & status;
+
+ /* Don't copy more bytes than there is room for in the buffer */
+ count = sci_rxfill(port);
+ if(count >= sport->rx_trigger)
+ count--;
+
+ count = tty_buffer_request_room(tport, count);
+
+ /* If for any reason we can't copy more data, we're done! */
+ if (count == 0)
+ goto next;
+
+ if (port->type == PORT_SCI) {
+ char c = serial_port_in(port, SCxRDR);
+ if (uart_handle_sysrq_char(port, c))
+ count = 0;
+ else
+ tty_insert_flip_char(tport, c, TTY_NORMAL);
+ } else {
+ for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
+ char c;
+
+ if (port->type == PORT_SCIF ||
+ port->type == PORT_HSCIF) {
+ status = serial_port_in(port, SCxSR);
+ c = serial_port_in(port, SCxRDR);
+ } else {
+ c = serial_port_in(port, SCxRDR);
+ status = serial_port_in(port, SCxSR);
+ }
+ if (uart_handle_sysrq_char(port, c)) {
+ count--; i--;
+ continue;
}
+
+ /* Store data and status */
+ if (status & SCxSR_FER(port)) {
+ flag = TTY_FRAME;
+ port->icount.frame++;
+ dev_notice(port->dev, "frame error\n");
+ } else if (status & SCxSR_PER(port)) {
+ flag = TTY_PARITY;
+ port->icount.parity++;
+ dev_notice(port->dev, "parity error\n");
+ } else
+ flag = TTY_NORMAL;
+
+ tty_insert_flip_char(tport, c, flag);
}
+ }
- serial_port_in(port, SCxSR); /* dummy read */
- sci_clear_SCxSR(port, SCxSR_RDxF_CLEAR(port));
+ serial_port_in(port, SCxSR); /* dummy read */
+ sci_clear_SCxSR(port, SCxSR_RDxF_CLEAR(port));
- copied += count;
- port->icount.rx += count;
- }
+ copied += count;
+ port->icount.rx += count;
+next:
if (copied) {
/* Tell the rest of the system the news. New characters! */
- tty_flip_buffer_push(tport);
+ if(rx_to)
+ tty_flip_buffer_push(tport);
} else {
/* TTY buffers full; read from RX reg to prevent lockup */
serial_port_in(port, SCxRDR);
@@ -2775,6 +2814,51 @@ static int sci_verify_port(struct uart_port *port, struct serial_struct *ser)
return 0;
}
+static int sci_swrts_ctl(struct uart_port *port, unsigned long arg)
+{
+ //struct circ_buf *xmit = &port->state->xmit;
+ struct sci_port *sport = to_sci_port(port);
+ int cmd, ret = 0;
+
+ if(!sport->rs485_sw_rts)
+ return 0;
+
+ cmd = arg & 0xff;
+
+ switch(cmd)
+ {
+ case SWRTS_GET_I: /* check rs485-sw-rts device */
+
+ return 1;
+
+ case SWRTS_SET_H:
+
+ gpio_set_value(sport->sw_rts_gpio, 1);
+
+ sport->sw_rts_count = (int)(arg >> 8);
+
+ break;
+
+ case SWRTS_SET_L:
+
+ /* Reset RTS GPIO to Low in SCIF TX Empty interrupt, not here */
+
+ if(down_interruptible(&sport->sw_rts_sema)) {
+ ret = -ERESTART;
+ break;
+ }
+
+ break;
+
+ default:
+
+ dev_err(port->dev, "unsupported cmd 0x%lx for %s\n", arg, __func__);
+ return -EPERM;
+ }
+
+ return ret;
+}
+
static const struct uart_ops sci_uart_ops = {
.tx_empty = sci_tx_empty,
.set_mctrl = sci_set_mctrl,
@@ -2798,6 +2882,7 @@ static const struct uart_ops sci_uart_ops = {
.poll_get_char = sci_poll_get_char,
.poll_put_char = sci_poll_put_char,
#endif
+ .swrts_ctl = sci_swrts_ctl
};
static int sci_init_clocks(struct sci_port *sci_port, struct device *dev)
@@ -3185,6 +3270,12 @@ static int sci_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
if (type == PORT_SCIFA || type == PORT_SCIFB || type == PORT_HSCIF)
device_remove_file(&dev->dev, &dev_attr_rx_fifo_timeout);
+ if(dev->dev.of_node)
+ {
+ if(port->rs485_sw_rts)
+ devm_gpio_free(&dev->dev, port->sw_rts_gpio);
+ }
+
return 0;
}
@@ -3307,6 +3398,29 @@ static struct plat_sci_port *sci_parse_dt(struct platform_device *pdev,
sp->has_rtscts = of_property_read_bool(np, "uart-has-rtscts");
+ sp->rs485_sw_rts = of_property_read_bool(np, "rs485-sw-rts");
+
+ if(sp->rs485_sw_rts)
+ {
+ sp->sw_rts_gpio = of_get_gpio(np, 0);
+
+ if(!gpio_is_valid(sp->sw_rts_gpio))
+ {
+ dev_err(&pdev->dev, "'sw_rts_gpio' invalid in device tree node\n");
+ return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
+ }
+
+ if(devm_gpio_request_one(&pdev->dev, sp->sw_rts_gpio, GPIOF_DIR_OUT, pdev->name) < 0)
+ {
+ dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Unable to request GPIO for sw rs485\n");
+ return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
+ }
+
+ gpio_direction_output(sp->sw_rts_gpio, 0); // output LOW(RS-485 INPUT Mode) first
+
+ sema_init(&sp->sw_rts_sema, 0);
+ }
+
return p;
}
drivers/tty/serial/sh-sch.h
diff --git a/drivers/tty/serial/sh-sci.h b/drivers/tty/serial/sh-sci.h
index c0ae78632dda..440b363d9362 100644
--- a/drivers/tty/serial/sh-sci.h
+++ b/drivers/tty/serial/sh-sci.h
@@ -80,6 +80,7 @@ enum {
#define SCI_RDxF_CLEAR (u32)(~(SCI_RESERVED | SCI_RDRF))
#define SCI_ERROR_CLEAR (u32)(~(SCI_RESERVED | SCI_PER | SCI_FER | SCI_ORER))
#define SCI_TDxE_CLEAR (u32)(~(SCI_RESERVED | SCI_TEND | SCI_TDRE))
+#define SCI_TEND_CLEAR (u32)(~(SCI_RESERVED | SCI_TEND))
#define SCI_BREAK_CLEAR (u32)(~(SCI_RESERVED | SCI_PER | SCI_FER | SCI_ORER))
/* SCxSR (Serial Status Register) on SCIF, SCIFA, SCIFB, HSCIF */
@@ -102,6 +103,7 @@ enum {
#define SCIF_RDxF_CLEAR (u32)(~(SCIF_DR | SCIF_RDF))
#define SCIF_ERROR_CLEAR (u32)(~(SCIF_PER | SCIF_FER | SCIF_ER))
#define SCIF_TDxE_CLEAR (u32)(~(SCIF_TDFE))
+#define SCIF_TEND_CLEAR (u32)(~(SCIF_TEND))
#define SCIF_BREAK_CLEAR (u32)(~(SCIF_PER | SCIF_FER | SCIF_BRK))
/* SCFCR (FIFO Control Register) */
@@ -173,5 +175,7 @@ enum {
(to_sci_port(port)->params->error_clear)
#define SCxSR_TDxE_CLEAR(port) \
(((port)->type == PORT_SCI) ? SCI_TDxE_CLEAR : SCIF_TDxE_CLEAR)
+#define SCxSR_TEND_CLEAR(port) \
+ (((port)->type == PORT_SCI) ? SCI_TEND_CLEAR : SCIF_TEND_CLEAR)
#define SCxSR_BREAK_CLEAR(port) \
(((port)->type == PORT_SCI) ? SCI_BREAK_CLEAR : SCIF_BREAK_CLEAR)
drivers/tty/tty_io.c
diff --git a/drivers/tty/tty_io.c b/drivers/tty/tty_io.c
index 669aef77a0bd..21f30a864cc1 100644
--- a/drivers/tty/tty_io.c
+++ b/drivers/tty/tty_io.c
@@ -514,6 +514,7 @@ static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(redirect_lock);
static struct file *redirect;
extern void tty_sysctl_init(void);
+extern int is_serial_core_tty(struct tty_struct *tty);
/**
* tty_wakeup - request more data
@@ -968,9 +969,12 @@ static inline ssize_t do_tty_write(
struct file *file,
struct iov_iter *from)
{
- size_t count = iov_iter_count(from);
+ size_t count = iov_iter_count(from), par;
ssize_t ret, written = 0;
unsigned int chunk;
+ int serial_core_tty;
+
+ serial_core_tty = is_serial_core_tty(tty);
ret = tty_write_lock(tty, file->f_flags & O_NDELAY);
if (ret < 0)
@@ -1015,6 +1019,14 @@ static inline ssize_t do_tty_write(
tty->write_buf = buf_chunk;
}
+ if(serial_core_tty) {
+ par = count << 8;
+ if(tty->ops->ioctl(tty, TIOCSSWRTS, SWRTS_SET_H | par)) {
+ ret = -ERESTART;
+ goto out;
+ }
+ }
+
/* Do the write .. */
for (;;) {
size_t size = count;
@@ -1045,6 +1057,14 @@ static inline ssize_t do_tty_write(
break;
cond_resched();
}
+
+ if(serial_core_tty) {
+ if(tty->ops->ioctl(tty, TIOCSSWRTS, SWRTS_SET_L)) {
+ ret = -ERESTART;
+ goto out;
+ }
+ }
+
if (written) {
tty_update_time(&file_inode(file)->i_mtime);
ret = written;
include/linux/serial_core.h
diff --git a/include/linux/serial_core.h b/include/linux/serial_core.h
index 35b26743dbb2..783608a94437 100644
--- a/include/linux/serial_core.h
+++ b/include/linux/serial_core.h
@@ -80,6 +80,7 @@ struct uart_ops {
void (*poll_put_char)(struct uart_port *, unsigned char);
int (*poll_get_char)(struct uart_port *);
#endif
+ int (*swrts_ctl)(struct uart_port *, unsigned long);
};
#define NO_POLL_CHAR 0x00ff0000
include/uapi/asm-generic/ioctls.h
diff --git a/include/uapi/asm-generic/ioctls.h b/include/uapi/asm-generic/ioctls.h
index cdc9f4ca8c27..6dde21d68cff 100644
--- a/include/uapi/asm-generic/ioctls.h
+++ b/include/uapi/asm-generic/ioctls.h
@@ -106,6 +106,18 @@
# define FIOQSIZE 0x5460
#endif
+/*
+ * Add ioctl commands for software RS-485 RTS control
+ */
+#define TIOCSSWRTS 0x5500
+enum
+{
+ SWRTS_GET_I = 0, /* Get software RS-485 RTS device support info */
+ SWRTS_SET_H, /* Set RTS GPIO to HIGH */
+ SWRTS_SET_L /* Set RTS GPIO to LOW */
+};
+
+
/* Used for packet mode */
#define TIOCPKT_DATA 0
#define TIOCPKT_FLUSHREAD 1
Kernel Networking Configurations
Add iptables support
When using iptables command, below error occurs.
root@smarc-rzg2ul:~# iptables -L modprobe: FATAL: Module ip_tables not found in directory /lib/modules/5.10.83-cip1-yocto-standard iptables v1.8.4 (legacy): can't initialize iptables table `filter': Table does not exist (do you need to insmod?) Perhaps iptables or your kernel needs to be upgraded.
Please use below bitbake command to change the kernel configuration:
# command to open the menuconfig tool $ bitbake linux-renesas -c menuconfig
Please change enable below kernel configuration:
[*] Networking support --->
Networking options --->
[*] Network packet filtering framework (Netfilter) --->
Core Netfilter Configuration --->
<*> Netfilter connection tracking support
IP: Netfilter Configuration --->
<*> IP tables support (required for filtering/masq/NAT)
<*> Packet filtering
<*> iptables NAT support
<*> MASQUERADE target support
After the kernel configuration was fixed, please use bitbake to start the build progress.
# start the system build with bitbake command $ bitbake core-image-<minimal/bsp/weston/qt>
Add ip6tables support
If the below error happened when using ip6tables command, users can fix it by changing kernel configuration.
# error logged when using command "ip6tables" root@smarc-rzg2ul:~# ip6tables -L modprobe: FATAL: Module ip6_tables not found in directory /lib/modules/5.10.83-cip1-yocto-standard ip6tables v1.8.4 (legacy): can't initialize ip6tables table `filter': Table does not exist (do you need to insmod?) Perhaps ip6tables or your kernel needs to be upgraded.
Kernel configuration to support ip6tables.
[*] Networking support --->
Networking options --->
<*>The IPv6 protocol --->
[*] Network packet filtering framework (Netfilter) --->
IPv6: Netfilter Configuration --->
<*> IP6 tables support (required for filtering)
<*> Packet filtering
<*> ip6tables NAT support
<*> MASQUERADE target support
Add ip support
When using ip command to configure the VLAN on RZ/G device, the below error message may occur.
root@smarc-rzg2ul:~# ip link add link eth0 name eth0.100 type vlan id 100 Error: Unknown device type.
Please change the kernel configuration as below and restart the build progress.
[*] Networking support --->
Networking options --->
<*> 802.1Q/802.1ad VLAN Support
[*] GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol) support
[*] MVRP (Multiple VLAN Registration Protocol) support
Helpful Networking Packages
Following packages can be installed in the system to improve the functionality of networking
DHCP Support
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks for automatically assigning IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices.
dhcp
To add dhcp server and client, please add below code to local.conf:
CORE_IMAGE_EXTRA_INSTALL_append = " dhcp-libs dhcp-server dhcp-server-config dhcp-client dhcp-relay dhcp-omshell "
kea
kea is a successor of ISC-DHCP(Internet Systems Consortium - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) for high performance and extensible DHCPv4/DHCPv6 server.
Currently, with ISC DHCP, which is widely used by ISPs and companies, it was necessary to restart the server when changing settings, but with Kea DHCP, changes can be reflected without restarting the server.
To add kea package to rootfs, please add this code to local.conf:
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " kea "
bridge-utils
The bridge-utils package contains a utility needed to create and manage bridge devices on RZ/G2 boards.
A bridge is a type of software used to bind multiple network segments together. The bridge acts like a virtual network switch and works transparently (other machines don't need to know it exists). You can connect real devices (eg eth0) and virtual devices (eg tap0) to the bridge.
To install the bridge-utils package, you can add "bridge-utils" to IMAGE_INSTALL_append variable in local.conf.
# in local.conf IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " bridge-utils "
NOTE: User may need to enable both ethernet ports on an EVK. Please refer chapter "Add ipatbles support".
To enable the support of bridge function, below kernel configuration should be added with command "bitbake linux-renesas -c menuconfig".
$ bitbake linux-renesas -c menuconfig
[*] Networking support --->
Networking options --->
[*] Network packet filtering framework (Netfilter) --->
<*> Bridged IP/ARP packets filtering
Core Netfilter Configuration --->
<*> Netfilter Xtables support (required for ip_tables)
<*> Ethernet Bridge tables (ebtables) support --->
<*> ebt: broute table support
<*> ebt: filter table support
<*> ebt: nat table support
<*> ebt: 802.3 filter support
<*> ebt: among filter support
<*> ebt: ARP filter support
<*> ebt: IP filter support
<*> ebt: limit match support
<*> ebt: mark filter support
<*> ebt: packet type filter support
<*> ebt: STP filter support
<*> ebt: 802.1Q VLAN filter support
<*> ebt: arp reply target support
<*> ebt: dnat target support
<*> ebt: mark target support
<*> ebt: redirect target support
<*> ebt: snat target support
<*> ebt: log support
<*> 802.1d Ethernet Bridging
When kernel configuration is edited, issue command to enable system build.
bitbake core-image-<minimal/bsp/weston/qt>
Users can set a bridge with the command brctl on EVK.
# set a bridge br0 $ brctl addbr br0 # Add port eth0 and eth1 to bridge br0 $ brctl addif br0 eth0 eth1 # set ip address for br0 $ ifconfig br0 192.168.10.200
rp-pppoe and rp-pppoe-server
RP-PPPoE is a PPPoE client, relay and server for Linux. It can run completely in user-mode or used the Linux kernel's built-in PPPoE support. Here is the homepage of RP-PPPoE project.
You can enable pppoe client and server by adding the code below to local.conf:
# code to enable pppoe client and server in local.conf IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " rp-pppoe rp-pppoe-server "
To enable pppoe function, following kernel configuration must be enabled.
Device Drivers --->
[*] Network device support --->
<*> PPP (point-to-point protocol) support
<*> PPP over Ethernet
<*> PPP support for async serial ports
<*> PPP BSD-Compress compression
<*> PPP Deflate compression
<*> PPP support for sync tty ports
Character devices --->
[*] Non-standard serial port support
<*> HDLC line discipline support
Network Manager
NetworkManager is a system service that manages network interfaces and connections based on user or automatic configuration. It supports Ethernet, Bridge, VLAN, Wi-Fi, PPPoE and other devices, and supports a variety of different VPN services.
NOTE: Networkmaneger packages and its dependencies require removing the restriction on GPLv3 and GPLv3+ license.
To enable networkmanager in rootfs image, please add the below code to local.conf.
# add networkmaneger IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " networkmanager " # Exclude packages for networkmanager PACKAGE_EXCLUDE = " connman connman-client connman-tests connman-tools connman-t-online " # Comment out the restriction on GPLv3 and GPLv3+ license #INCOMPATIBLE_LICENSE = "GPLv3 GPLv3+"
vlan
VLAN (Virtual LAN) is a technology that creates a virtual LAN segment independent of the physical connection form. VLANs are used to logically divide LAN segments inside the switch. By using VLAN broadcast domains can be divided with L2 switches in the same way as with routers and L3 switches.
To add vlan to rootfs image, please add below code to local.conf.
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " vlan "
To enable routing between the different vlans, please run the below command on the evaluation board:
# Enable ip forward to enable routing between vlans $ echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
tcpdump
tcpdump is a powerful command-line packet analyzer. It allows the user to display TCP/IP and other packets being transmitted or received over a network.
To enable this package in rootfs image, please use the below code in local.conf:
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " tcpdump "
WiFi Support
The following packages are for the Wifi support on RZ/G board.
Enable Wireless in Kernel
On RZ/G2L series board, user will need WiFi adapter the WiFi adapter used by us is BUFFALO WLI-UC-G301N. Wifi adapters requires support from kernel. Please enable the below kernel configuration.
Device Drivers ---> [*] Network device support ---> <*> USB Network Adapters ---> <*> Multi-purpose USB Networking Framework
Device Drivers --->
[*] USB support --->
<*> USB Wireless Device Management support
Please set the wireless configuration as below:
Networking support --->
[*] Wireless --->
<*> cfg80211 - wireless configuration API
[*] nl80211 testmode command
[*] enable developer warnings
[*] enable powersave by default (NEW)
[*] cfg80211 DebugFS entries
[*] cfg80211 wireless extensions compatibility
<*> Generic IEEE 802.11 Networking Stack (mac80211)
Default rate control algorithm (Minstrel) --->
[*] Enable mac80211 mesh networking support
[*] Enable LED triggers
[*] Export mac80211 internals in DebugFS
[*] Trace all mac80211 debug messages
[*] Select mac80211 debugging features --->
crda
This is the Central Regulatory Domain Agent for Linux. It serves one purpose: tell Linux kernel what regulatory rules to enforce for 802.11. CRDA searches for available frequency bands in the regulatory information database provided by the wireless-regdb package.
When using Wifi adapter from TP-Link without this package, user will see kernel message:
cfg80211: failed to load regulatory.db
Please add this package with the code below to remove the above error message:
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " crda "
hostapd
hostapd (host access point daemon) is a user space daemon software enabling a network interface card to act as an access point and authentication server.
Let RZ/G board be a Wifi access point. Please add the code in local.conf:
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " hostapd "
Please add settings for adapter to hostapd file /etc/hostapd.conf
# in file /etc/hostapd.conf interface=wlan0 driver=nl80211 ssid=<Wifi SSID> hw_mode=g channel=1 wmm_enabled=1 macaddr_acl=0 auth_algs=1 wpa=2 wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK rsn_pairwise=CCMP wpa_passphrase=<Wifi password>
To check the setting in file /etc/hostapd.conf, please use the below command. There should be no error message if the setting was correct.
# Check settings in file /etc/hostapd.conf $ hostapd -dd /etc/hostapd.conf
Users can start/stop hostapd manually with the below command:
# Start the hostapd service $ systemctl start hostapd # Stop the hostapd service $ systemctl stop hostapd
iw (wireless tools)
To offer support for 802.11 standard WLAN settings, iw package is provided as wireless tool and can be installed with the code below in local.conf:
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " iw "
linux-firmware
linux-fiemware is a package distributed together with the Linux kernel that contains the firmware binary blobs necessary for the functioning of a particular hardware device.
Use below code to add this package:
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " linux-firmware "
wpa-supplicant
wpa_supplicant is a cross-platform supplicant that supports WEP, WPA, WPA2 (IEEE 802.11i / RSN (Robust Secure Network)). It targets desktops, laptops and embedded systems.
Please add this package with below code:
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " wpa-supplicant "