RZ-Five/RZ-Five-BSP Porting
This page is to highlight important things to consider when porting the Renesas BSP to your own custom board.
The steps explained in this page are similar to what described for the Arm based devices (RZ/G2). To avoid duplications, the focus is on the differences, then you can refer to the RZ/G2 pages for anything common.
Overview
One preliminary point to underline, true also for Arm based devices, is that you may NOT want to use Yocto at the beginning, rather clone the repositories, modify the code and build it using a cross toolchain.
The toolchain itself is a point to discuss a bit more in depth, since RISC-V ecosystem is still not as mature as Arm's.
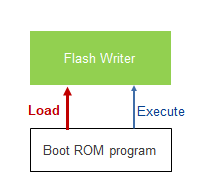
The paragraph order in this page is intentional. Similarly to what explained for Arm based device, they represent the steps you normally do when you want to port the Renesas BSP, i.e. you absolutely want to start from Flash Writer. When you get your first custom board samples the non-volatile memories are virgin and the first goals is to program them with bootloaders. One of the first thing you need to do is to adjust the DDR configuration to your own. Debugging DDR may be tricky but have it working is a major step toward success. You can test the DDR using some hidden Flash Writer commands. After that you may need to change the SPI configuration.
Then you can use Flash Writer to program the bootloaders: u-boot SPL (Secondary Program Loader), Open SBI (Supervisor Binary Interface and u-boot. Bootloaders can be programmed into QSPI FLASH or eMMC, then of course the boot mode of the SoC shall be adjusted accordingly. u-boot-spl may also need to be configured depending on the non-volatile memory type. Normally you do not need to program separately (e.g. different files for each boot loader), only two files u-boot-spl and u-boot.itb are needed but the Open SBI binary has to be included before building u-boot.
Some modifications may be needed in u-boot-spl. One of the first things spl does is to configure the DDR. You would need to use the same (working) configuration used with Flash Writer, so there should be no surprise here, if the DDR works with Flash Writer then it will work with ATF as well.
 -------------------------------
------------------------------- 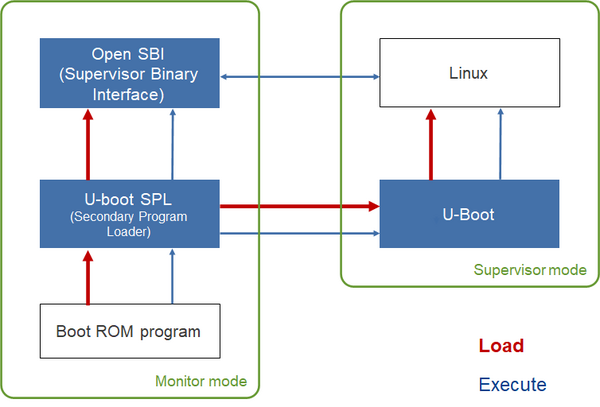
Then u-boot-spl loads Open SBI and u-boot, from either QSPI or eMMC. Assuming everything goes fine u-boot prompt is finally reachable.
The next step is to port the Linux CIP Kernel, by "porting" we mainly mean that the reference board device tree gets modified to reflect the HW available on the custom board.
Finally you can use Yocto to generate the root file system including all the bits and bobs you need to run your custom application.
Toolchain
- TBD
Flash Writer
Porting Flash Writer to RZ/Five is almost identical to RZ/G2L. Please refer to this page for more details. Of course some of the steps need to be adapted:
- The branch to be selected is different:
git checkout origin/rz_g2l
- param_mc.c should be copied in the ddr/five folder
u-boot-spl
- RZ-Five/RZ-Five BSP_Porting_SPL
Open SBI
- RZ-Five/RZ-Five BSP_Porting_SBI
u-boot
- RZ-Five/RZ-Five BSP_Porting_u-boot
Linux Kernel
Yocto
Memory Map
- This section explains how DDR Memory is divided and configured.
- TBD
Github Repositories
- This section explains the purpose of each github repository and branch.
- RZ-G/RZ-G2_BSP_GithubRepos

